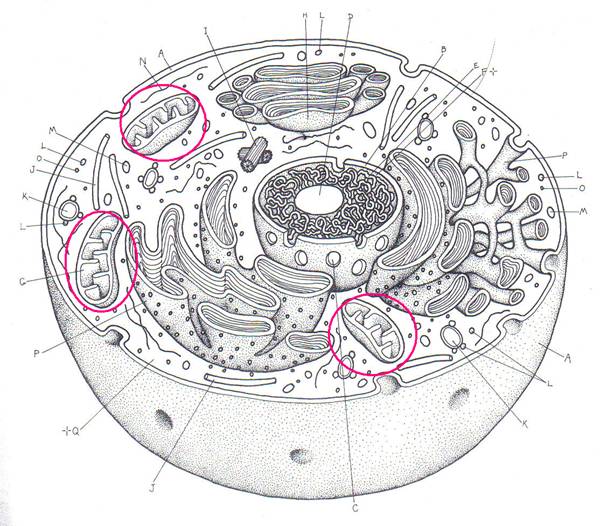
1.
Name this organelle.
2. Give its
function.
CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTUE AND TRANSPORT CARD REVIEW
(we did this in class)
Complete using your answer sheet
 |
1.
Name this organelle.
2. Give its
function.
|
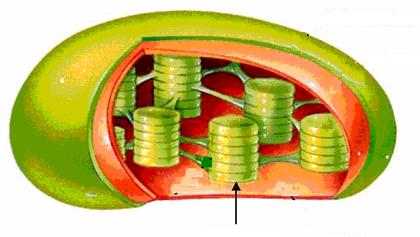 |
3. These membrane sacs are called ________. |
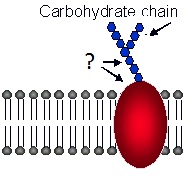 |
4. Name these integral
proteins found in cell membranes help in identification. |
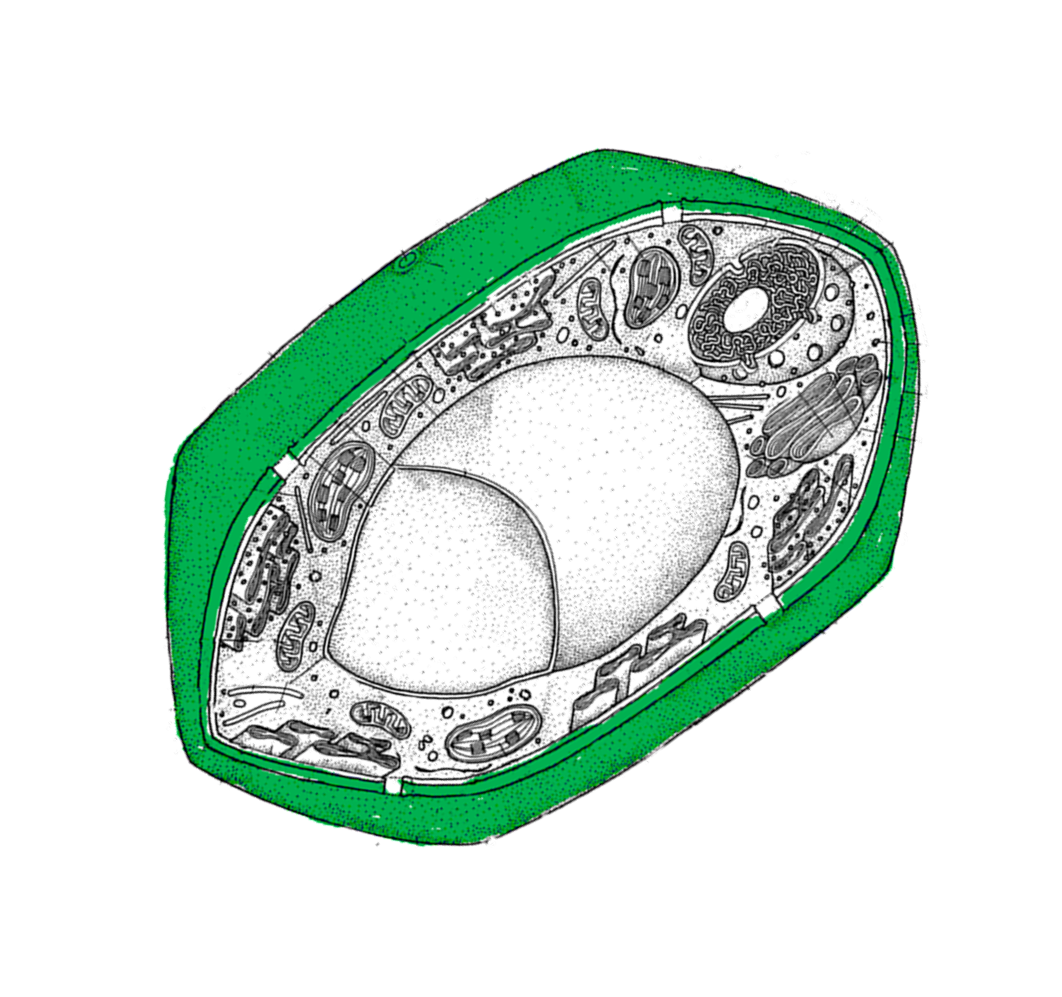 |
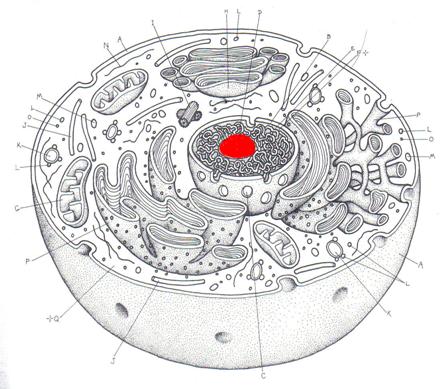
5. Name this
colored cell
part. |
6. Tell the polysaccharide found in
PLANT CELL WALLS that makes them sturdy.
7. Membranes that allow certain
substances to pass through, but keep others out are said to be ________________
_______________.
8.
The folded membranes inside a mitochondrion are called ________.
9. The DNA and attached proteins that
are SCRUNCHED UP in DIVIDING cells are called _________.
10.
The PROTEINS that are used to make the cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, and
centrioles are called _______.
 |
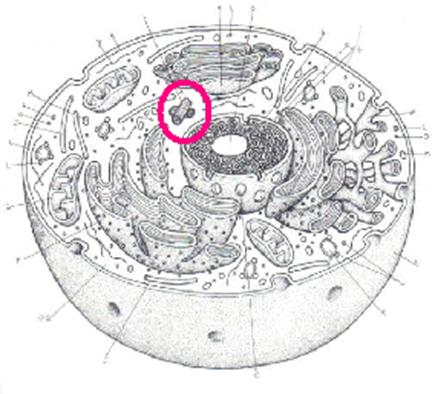
11.
Name this colored organelle |
13.
Ribosomes can be found attached to _______.
14.
Membrane proteins that stick into the cell membranes either part way or all the
way through the cell membrane are called __________ proteins.
15.
________________ and ____________ are the two main molecules that make up cell
membranes.
16.
________________ are the smallest kind of cell.
Plant
cells
Animal cells
Bacterial cells
17.
The gel-like fluid and the organelles it contains which is found inside the cell
membranes is called ______________________.
18. An
organism with a nuclear membrane and membrane bound organelles is called a
__________________________________.
19.
Name an organelle BESIDES THE NUCLEUS that has a DOUBLE MEMBRANE AND ITS OWN
DNA.
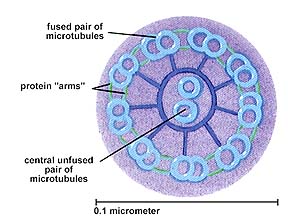 |
20.
Name an organelle that has this arrangement of microtubules. |
21.
Name a part found in plant cells but not animal or bacterial cells.
22.
Which part acts as the UPS/post office of the cell to sort, modify, and package molecules
for storage or transport out of cell?
 |
23. Name this part
24.
Tell what it does |
25.
Name a kind of cell that is a EUKARYOTE.
26.
Tell one way animal cells are different from bacterial cells.
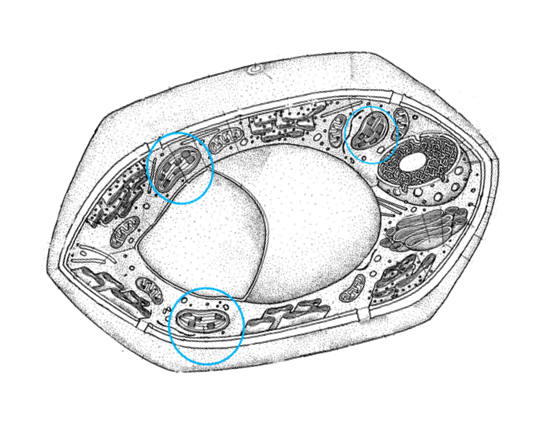 |
27. Name this part
28. Give its
function |
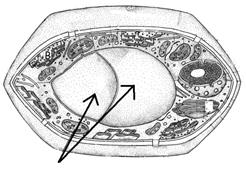 |
29. Name this part
30. Give a function |
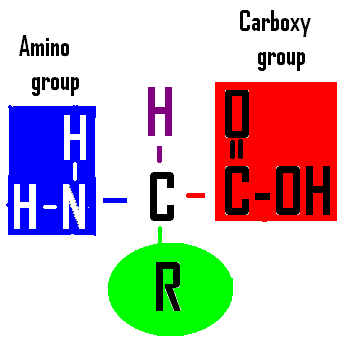 |
32. Name the cell part that joins subunits like these to make a macromolecule. |
33.
When water enters a plant cell the osmotic pressure inside will _______.
increase OR
decrease
 |
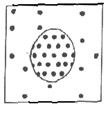
34. The dots in this diagram represent dissolved solute molecules. This diagram represents a cell placed in a ______ solution.
hypotonic
isotonic
hypertonic
35. The cell in the
diagram will _____.
shrink
swell & possibly burst
stay the same size |
 |
36.
The swelling and possibly bursting of an animal cell when placed
in a HYPOTONIC solution is called _______________.
plasmolysis
cytolysis
crenation |
 |
37.
The dots in this diagram represent dissolved solute molecules.
This diagram represents a cell placed in a _________ solution.
hypotonic
isotonic
hypertonic
38.
The “cell” in the diagram will _________.
shrink
swell & burst
stay the same size |
39.
The diffusion of WATER from high concentration to LOW concentration
across a semi-permeable membrane is called ________.
 |
40.
The shrinking of an animal cell when placed in a HYPERTONIC
solution is called ____________.
plasmolysis
cytolysis
crenation |
41. If a cell is in a ______________ liquid, the concentration of solute inside the cell and outside the cell are EQUAL.
42. Name the transport proteins that help water molecules get aross cell membranes.
43.
Molecules will automatically move from an area with _______ concentration
to an area of ________ concentration.
low to high
high to low
 |
44.
Plasmolysis happens to plant cells placed in a ______ solution.
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
|
1. Mitochondria
2. Powerplant/Burn glucose/make ATP
3. Thylakoids
4. Glycoproteins
5. Cell wall
6. cellulose
7. Selectively Permeable OR
Semi-permeable
8. Cristae
9. Chromosomes
10. Microtubules
11. Nucleolus
12. Make ribosomes (RNA)
13.
Rough ER
14. Integral
15. Phospholipids & proteins
16. BACTERIAL cells
17. cytoplamsm
18. Eukaryote
19. Mitochondria OR chloroplasts
20. 9 + 2 =Cilia or flagella
21. Chloroplast/cell wall/really big vacuole
22. Golgi
23. centrioles
24. Guide chromosomes apart during cell division
25. Plant or animal
26.
|
ANIMAL |
BACTERIA |
|
Nucleus |
No
nucleus |
|
Have
membrane bound organelles |
No
membrane bound organelles |
|
No
cell wall |
Have
a cell wall |
|
Centrioles |
No
centrioles |
|
Eukaryote |
Prokaryote |
27. chloroplast
28. photosynthesis
29, vacuole
30. Storage
31. Cilia- many, short/Flagella- few, long
32. RIBOSOMES use amino acids to make proteins
33. increase
34. hypertonic
35. shrink (Solute sucks!)
36. cytolysis
37. hypotonic
38. swell and burst (Solute sucks!)
39. osmosis
40. crenation
41. isotonic
42. Aquaporins
43. higher to lower
44. hypertonic
45. vesicle
CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CARD REVIEW
Complete using your answer sheet
 |
#1.
Name this organelle.
#2.
Give the function for #1.
|
 |
#3.These membrane sacs are called _________. |
| #4. These integral proteins found in cell membranes help in identification. | 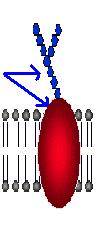 |
#5.
Name this organelle.
#6.
Tell the polysaccharide found in PLANT CELL WALLS that makes them sturdy.
#9.
The DNA and attached proteins that is SCRUNCHED UP in DIVIDING cells is called
______________
#10.
The PROTEINS that are used to make the cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, and
centrioles are called ___________________.
 |
#11.
Name this organelle. #12.
Give its function |
#13.
Ribsomes can be found attached to_____________.
#14.
Membrane proteins that stick into the cell membrane either part way or all the
way through are called
#15.
#16.
____________ are the smallest kind of cell.
Plant
cells
Animal cells
Bacterial cells
#17.
The gel-like fluid and the organelles it contains which is found inside the cell
membrane is called ____________________.
#18.
An organism with a nuclear membrane and membrane bound organelles is called a
_________________.
#19.
Name the 2 organelles BESIDES THE NUCLEUS that have a DOUBLE MEMBRANE AND their
OWN DNA.
| #20. Name an organelle that has this arrangement of microtubules. | 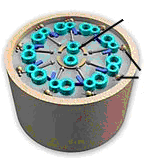 |
#21.
Name a part found in plant cells but not animal or bacterial cells.
#22.
Which part acts as the UPS of the cell to sort, modify, and package molecules
for storage or transport out of cell?
 |
#23.
Name this part. #24. Tell what it does. |
#25.
Name a kind of cell that is a EUKARYOTE.
#26. Tell one way animal cells are different from bacterial cells.
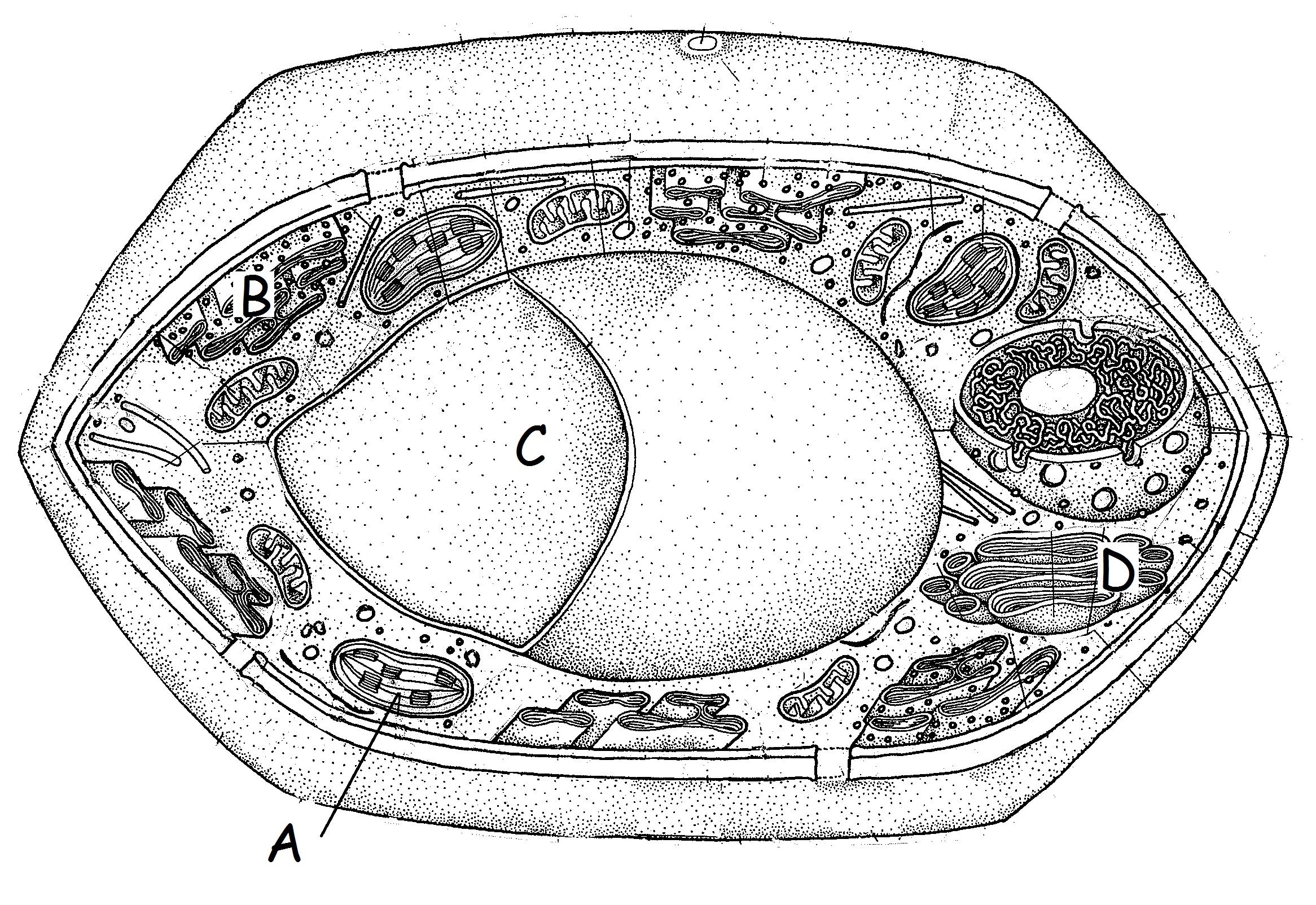 |
#27. Name A. #28. Give its function.
|
|
#29.
Name C #30. Tell something that might be found inside C.
|
 |
 |
#32. Name the cell part that uses this molecule. |
1. Mitochondria
2. Powerplant/Burn glucose/make ATP
3. Thylakoids
4. Glycoproteins
5. Cell wall
6.cellulose
7. Permeable
8. Cristae
9. Chromosomes
10. Microtubules
11. Nucleolus
12. Make ribosomes (RNA)
13. Rough ER
14. Integral
15. Proteins
16. BACTERIAL cells
17.cytoplamsm
18. Eukaryote
19. Mitochondria OR chloroplasts
20. 9 + 2 =Cilia or flagella
21. Chloroplast/cell wall/really big vacuole
22. Golgi
23.centrioles
24. Guide chromosomes apart during cell division
25. Plant or animal
26.
|
ANIMAL |
BACTERIA |
|
Nucleus |
No
nucleus |
|
Have
membrane bound organelles |
No
membrane bound organelles |
|
No
cell wall |
Have
a cell wall |
|
Centrioles |
No
centrioles |
|
Eukaryote |
Prokaryote |
27. chloroplast
|28. photosynthesis
29, vacuole
30. Water, food, waste, enzymes
31. Cilia- many, short/Flagella- few, long
32. RIBOSOMES use amino acids to make proteins